
In this way, capital investment can be minimized in undesirable stock. It is in the best interest of the organization to compare the turnover of different types of (and grades of) material as a measure of detecting stock that does not move regularly. As such, inventory turnover refers to the movement of materials into and out of an organization. The turnover of inventory ratio is closely tied to the days inventory outstanding (DIO) metric, which measures the number of days needed by a company to sell off its inventory in its entirety.Inventory turnover is the rate at which a company sells its inventory. Are there any specific products that have lost a substantial amount of consumer demand as of late? Which specific products have been selling out quickly and causing lost revenue (and vice versa)? Have recent purchases referenced historical customer demand patterns? Does the revenue generated from the sale of proceeds offset the expenses to be profitable? Is the company pricing its products at a competitive rate where there is sufficient customer demand? Some examples of practical diligence questions to ask (or answer) from assessing a company’s inventory management are the following: Rather than being a positive sign, high turnover could mean that the company is missing potential sales due to insufficient inventory. back orders, delayed deliveries, and speed) must be evaluated to understand the reality of the circumstances, as well as to see if there is an adverse impact on revenue. In such cases, the amount of pent-up demand (i.e. However, if a company’s inventory has an abnormally high turnover, it could also be a sign that management is ordering inadequate inventory as opposed to managing inventory well. That said, low turnover ratios suggest lackluster demand from customers and the build-up of excess inventory.įor example, retailers are typically known for exhibiting high turnover ratios – in particular, “fast-fashion” retailers like Zara are highly regarded for their ability to research trends and clear out their inventory quickly.
#INDUSTRY INVENTORY TURNOVER RATIO HOW TO#
How to Interpret Inventory Turnover Period?Ĭomparing a company’s ratio to its industry peer group can provide insights into how effective management is at inventory management.įor companies with low turnover ratios, the duration between when the inventory is purchased, produced/manufactured into a finished good, and then sold is more prolonged (i.e. The company’s inventory, if left unsold, might eventually need to be written down to reflect the true (lower) value on the balance sheet.

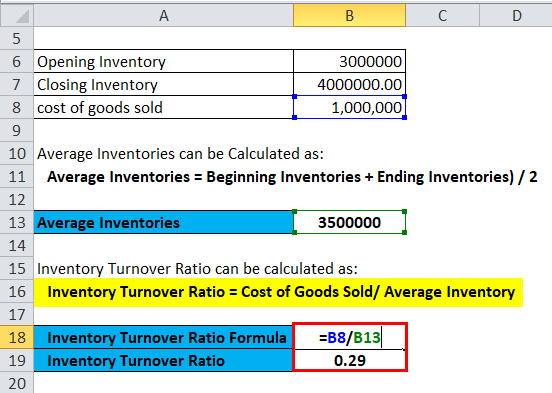
Inventory Turnover Ratio = Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) ÷ Average Inventory The formula used to calculate a company’s inventory turnover ratio is as follows. Step 2 → Divide the numerator, the cost of goods sold (COGS) in the corresponding period, by the average inventory as calculated above.Step 1 → Calculate the average inventory by adding the prior period inventory balance and ending inventory and then dividing by two.

The steps for calculating the inventory turnover ratio are the following: Thus, the metric determines how long it takes for a company to sell its entire inventory (and need to place more orders).

The ratio is calculated by dividing the cost of goods sold (COGS) by the average inventory balance for the matching period. In other words, the ratio measures how well a company can convert its inventory purchases into revenue. The inventory turnover ratio portrays the efficiency at which the inventory of a company is turned into finished goods and sold to customers. How to Calculate Inventory Turnover Ratio? The Inventory Turnover Ratio measures the number of times that a company replaced its inventory balance across a specific time period.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
